Molar Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Symptoms, Treatments, And More
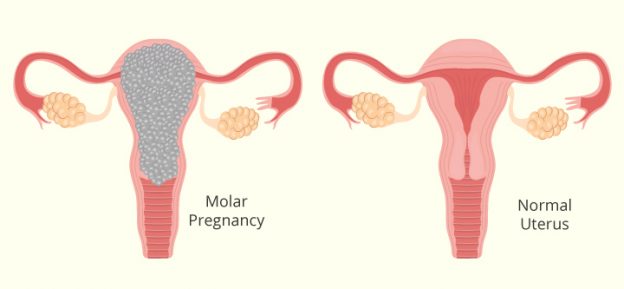
Molar Pregnancy of Hydatidiform Mole, is an abnormal growth of trophoblasts. This is a complicated case of pregnancy. Here the cells which are present in the placenta, spurt unusually. There is a complete and partial type of molar pregnancy. In the former, the placenta tissue swells having cysts filled with water.
There is no foetal tissue here. In the partial molar pregnancy, the placental tissue forms along with the abnormal development of cells. Here, a foetus may form, but it cannot survive. This can lead to a miscarriage. Such a kind of pregnancy is rare but possible. It may develop into cancer, and needs timely treatment.
In the following post, we will discuss causes, complications, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and support tips for a molar pregnancy.
Causes for Molar Pregnancy
The cause for such kind of pregnancy is due to abnormal fertilization of the egg. But who will you distinguish between normal and abnormal fertilization of egg? The human cells usually have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Each pair has one chromosome that comes from mother and father.
In a molar pregnancy (complete), one or two sperm fertilizes an empty egg. The genetic composition here belongs only to the father. Thus, there is an absence of chromosomes from the mother. The father’s chromosomes then duplicate, leading to unusual fertilization.
In a partial molar pregnancy, two sets of chromosomes come from the father. The mother’s chromosomes also exist. Because of this, the embryo has a composition of 69 chromosomes. But the normal count of chromosomes should be 46. This happens when two sperm fertilize an egg.
As there is more than a copy of genetic material from the father, abnormal fertilization occurs. In both cases, the foetus will face difficulties. It is best to consult a doctor to understand which type of (partial or complete) hydatidiform mole the foetus possesses.
Complications
It is important to remove the affected foetus. Full growth of pregnancy is not advisable as it is life-threatening. Even after the complete removal of tissues, in some cases, biological parts may remain. These may, unfortunately, continue to grow. Such a condition is GTN (gestational trophoblastic neoplasia).
A symptom of GTN is a high level of HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) even after ending the pregnancy. HCG is a pregnancy hormone. The frequency of GTN is 15% to 20% for complete molar pregnancies. For partial molar pregnancies, the same is 5%.
In a rare instance, GTN can turn to a cancerous formation – choriocarcinoma. The risk for choriocarcinoma is higher in complete molar pregnancy than a partial one. This can spread to other parts of the body. Cancer medications may successfully treat this condition.
Vaginal bleeding may happen. This is true when an invasive hydatidiform mole cuts deep into the uterus wall or the middle layer of it. Chemotherapy can treat persistent gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Another option is hysterectomy, which is complete uterus removal.
Molar Pregnancy Symptoms
It is not evident at first if a pregnancy is normal or molar. However, a few symptoms can assert the last. These include:
- Pain or pressure in the pelvic area
- Severe vomiting and nausea
- Discharge of Grape-sized cysts from the vagina
- In the first trimester, red or dark brown vaginal bleeding
In case of these signs, check with your healthcare provider to detect a molar pregnancy. Some of the indications the doctor may look for are:
- Uterus getting larger than normal for the current stage of pregnancy
- Preeclampsia – increases protein in urine and high blood pressure post 20 weeks of pregnancy
- Anaemia
- High blood pressure
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
- Ovarian cysts
Risk Factors
The occurrence of molar pregnancy is possible for 1 in every 1000 pregnancies. Some of the reasons for this are:
History of Molar Pregnancy
If in the past you experienced a similar pregnancy, the chances of facing it again are more. A repeat instance happens usually for 1 in 100 cases.
Age of the Female
Women older than 35 years of age or younger than 20 years of age are at a higher risk of this kind of pregnancy.
Detection
Here are some of the alternatives for diagnosis:
Series of Tests
If the doctor thinks you have a molar pregnancy, then he/she may suggest blood tests. These will look into the level of HCG in the blood. Next, you may have to get a transvaginal ultrasound soon.
Transvaginal Ultrasound
Here, the technician will direct high-frequency sound waves to your pelvic and abdominal area. The ultrasound includes a wand-like device. The doctor will place it in the vagina to see the internal tissues and more. In early pregnancy, the fallopian tubes and uterus are closer to the vagina.
These are not so close to the abdominal surface. A transvaginal ultrasound can detect this distance and confirm the stage of pregnancy. You can go for this diagnosis as early as 8 to 9 weeks of conceiving. For a complete molar pregnancy, the results will usually show:
- The uterus will have a thick cystic placenta
- No amniotic fluid
- Ovarian cysts
- No foetus or embryo
- On the other hand, a partial molar pregnancy may show results such as:
- Less amniotic fluid
- Abnormal placenta
- Unusually small foetus according to the gestational age
If the doctor detects the abnormal pregnancy, he/she may suggest running tests for other issues such as:
- Anaemia
- Preeclampsia
- Hyperthyroidism
Treatment
It is not suggested to continue a molar pregnancy. Thus, it is necessary to remove the abnormal placenta tissue from the uterus. There are many successful and safe ways to do so:
Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
In D&C, the doctor removes the molar tissues from the uterus. This procedure has to take place in an observation. So, you may have to admit yourself to the respective clinic or hospital. You will receive general or local anaesthesia during the surgery. The nurse will position you comfortably on the operating table.
Your back will rest on the bed usually in a raised position. Also, your legs will remain in stirrups. The surgeon will then insert a speculum into the vagina. This will give him/her access to the cervix. Before doing so, the doctor will dilate the cervix with numbing and ripening medicine.
By doing so, it gets easier to remove the uterine tissue. The molar tissues are then removable with the help of a vacuum device. The procedure takes hardly a few minutes to complete. It is painless apart from few cramps and slight vaginal bleeding. You can mostly return home the same day.
Monitor the HCG Level
Even after the removal of the pregnancy, the doctor will ask to monitor the HCG level after an interval. If the presence of HCG is still in the blood, you have to go through more treatment. After this, the same needs to be monitored every 6 months for at least a year.
This is to ensure that there is no existing molar tissue. Also, this will keep in check any unusual growth in the uterus. To stop a pregnancy from taking place, you can take birth control. Consult your physician about the suitable contraception options as per your health.
Hysterectomy
You can even opt for removal of the uterus entirely. Especially, if a person does not want to conceive anymore, this is one of the choices.
Prevention and Support Tips
You must talk to your doctor before conceiving again if in the past you had a molar pregnancy. Though the event does not need to reoccur, it is better to avoid risks. Timely blood tests, ultrasounds can keep your pregnancy in check. You can even go for prenatal genetic testing as a precaution.
Those who had to end their pregnancies due to a medical issue have a lot to face. It is understandable how devastating things can get. If you need someone to talk to, it is not wrong to do so. Look for friends, partners, family for support. You can also visit a counsellor to discuss your emotions.
Before visiting a doctor, keep a note of symptoms you are experiencing, including your feelings. Keep a list of medicines you take, even if it any OTC product. Remember to talk about any existing medical condition you have. If you know when you last menstruated, note down the date for it.
The physician will assess your health. He/she may prescribe a few tests as well if necessary. If you need a counsellor, he/she may recommend one. You can discuss the treatments to seek. Also, know how to approach any future pregnancy.
Also, Read Tips For Safe Pregnancy Workouts.
Final Thoughts
A molar pregnancy is uncommon to happen. But it is not unheard of. There is no need to panic if detected with this type of pregnancy. Seek timely treatment and aftercare. This will allow you to cope up with the procedure. You can look for support of any kind you wish after the treatment.
At the same time, take the prescribed medications on time. If you need to stall planning for conceiving for a few months or a year, then do so. This may be necessary for your well-being.
July 12, 2021 Sam Bell











Comments