Low Levels Of progesterone: Everything You Need To Know
Introduction
This article shall take you through the various symptoms of low levels of progesterone alongside its causes, complications, and treatments.
Progesterone is a female sex hormone. This sex hormone is involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and various other species. Progesterone plays a vital role in preparing the endometrium for pregnancy after ovulation.
Furthermore, this sex hormone then triggers the lining to thicken and to accept a fertilized egg. It also prohibits muscle contractions in the uterus as that would cause the body to reject the egg.
In layman’s terms, progesterone’s main job is to get the uterus ready for pregnancy. Since this hormone is very important during childbearing years, not having enough progesterone in the body may lead to trouble getting or staying pregnant.
Hence, it is always essential to diagnose the cause of low progesterone and treat it with the help of various medications and remedies that we have talked about in detail, in this article.
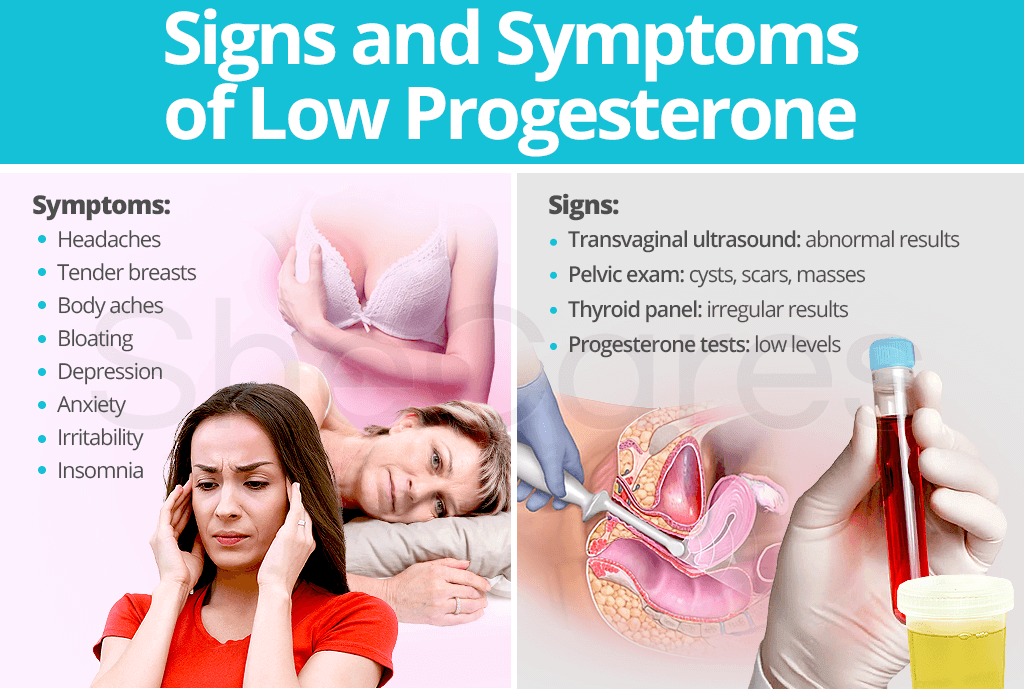
Symptoms of Low Progesterone
After one of the ovaries releases an egg, the progesterone levels should rise essentially in the female body.
As mentioned above, this hormone helps prohibit the muscle contractions in the uterus and allows the uterus to thicken in anticipation of receiving a fertilized egg.
If the uterus is not thick enough, the egg won’t be able to implant itself.
However, women who have low progesterone levels and yet succeed in getting pregnant are at a higher risk of the following:
Symptoms in women who are pregnant include:
- Spotting and miscarriage
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Recurrent pregnancy loss
- Pre-term delivery
Women, who aren’t pregnant but have low progesterone counts, may show symptoms too.
Symptoms in women who aren’t pregnant include:
- Mood changes
- Irregularity in the menstrual cycle
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Headaches or migraines
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
Causes of Low Progesterone
There are a variety of factors involved in causing low progesterone levels in women. Progesterone may be low if ovulation is not occurring regularly or sometimes if the body itself is not capable enough to build enough progesterone.
Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), elevated prolactin, and hypothyroidism, can cause infrequent or sometimes even absent ovulation, further leading to low progesterone levels in females.
In the above-mentioned cases, the cause of the low progesterone should be diagnosed and treated. Moreover, over-exercising, stress and obesity might hinder the balance between hormones and may cause lower progesterone levels.
It is always better to diagnose the main cause for progesterone’s low levels and get it treated.
Complications Caused by Low Progesterone
Low progesterone may sometimes lead to abnormal uterine bleeding in women who aren’t pregnant. Absent periods or irregular menstrual cycle is also a major complication that may indicate poorly functioning ovaries and low progesterone level in a female body.
An increased level of progesterone is also required once a female gets pregnant. Progesterone is required to maintain the proper functioning of the uterus until the baby is born.
Due to pregnancy, the body will automatically start producing even more progesterone which further might cause some of the symptoms of pregnancy, alongside breast tenderness and nausea.
If progesterone levels are too low, the uterus may not be able to carry the baby at all. As mentioned above, symptoms of low progesterone in pregnant women include spotting, miscarriage, and sometimes even pre-term delivery.
Low progesterone may sometimes also result in fetal death.
Without progesterone to complement it, estrogens might become the dominant hormone. This may cause symptoms like:
- Fibroids
- Mood swings
- Depression
- Breast tenderness
- Weight gain
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Anxiety
A progesterone test (PGSN) is required to fully know whether you have a low progesterone count or not.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Blood tests can detect low levels of progesterone, after which further tests can help determine the underlying cause.
Once the doctor has carried a PGSN test (progesterone test) and has announced that in fact, the body is running low on progesterone, further steps to treat it may include:
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Natural remedies
- Supplementation
1) Hormone Replacement Therapy
To treat severe symptoms of menopause, hormone therapy usually involves a combination of both estrogens and progesterone.
Moreover, hormone therapy may also additionally help in easing symptoms like dryness, hot flashes, and night sweats.
2) Natural Remedies
Intake of foods rich in vitamins B, C, and zinc is essential because they are necessary for maintaining proper progesterone levels.
Furthermore, controlling stress levels is also an imperative remedy to treat progesterone levels.
3) Supplementation
Supplementations include suppositories which are commonly used to treat progesterone levels in females.
Creams and gels, which can be used either topically or vaginally alongside various other oral medications.
Natural Progesterone Foods
Certain foods that may help in boosting progesterone levels are as follows
- Brussels sprouts
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- Kale
- Spinach
- Whole grains
- Beans
- Broccoli
- Nuts
Other Natural Remedies
- Stress is a prominent factor that triggers the production of stress hormones and further causes the kidneys to convert hormones like progesterone to cortisol.
- Several activities like meditation, listening to music, reading, and journaling can help relieve stress.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and body weight is essential in treating low progesterone levels in females.
- Apart from stress, over-exercising can also be seen as a factor in disturbing the balance between hormones.
Also, read our article, 9 progesterone side effects you should know about.
Conclusion
Progesterone is a female sex hormone and can cause different problems and show different symptoms in both, men and women. It’s always better to get the main cause of low progesterone levels diagnosed and treated with a specialist doctor’s help. Blood tests can detect low levels of progesterone, after which further tests can help determine the underlying cause.
April 12, 2021 Sam Bell











Comments