Implants And IUDs: Here’s Everything You Should Know About
In this post, we will discuss implants and IUDs, the similarities, differences, process of insertion/placement, how they work, who should not use, side effects, removal of the birth control device, and more.
Intrauterine Devices (IUD) and Hormonal implants are two common and effective types of birth control for women. These come under LARCs (Long-acting reversible contraceptives). Once you use any of these contraception methods, you stay protected from pregnancy for a good amount of duration.
Similarities Between Implants and IUDs
Birth control implants and intrauterine devices are effective in stopping pregnancy. The success rate is 99%. So, only 1 out of 100 women may conceive when on such a contraceptive. These are more successful than contraceptive pills. With pills, there are chances for 10 out of 100 females to conceive.
Both these birth controls are similar in other ways too:
- You must visit a doctor for the insertion of an IUD or implant.
- Also, only a medical professional can remove these.
- These contraception methods are reversible.
- You can conceive after the removal of an implant or IUD.
- Though more expensive than birth control pills, these are more long-lasting.
- Both however do not prevent sexually transmitted infections or diseases.
Differences Between Implants and IUDs
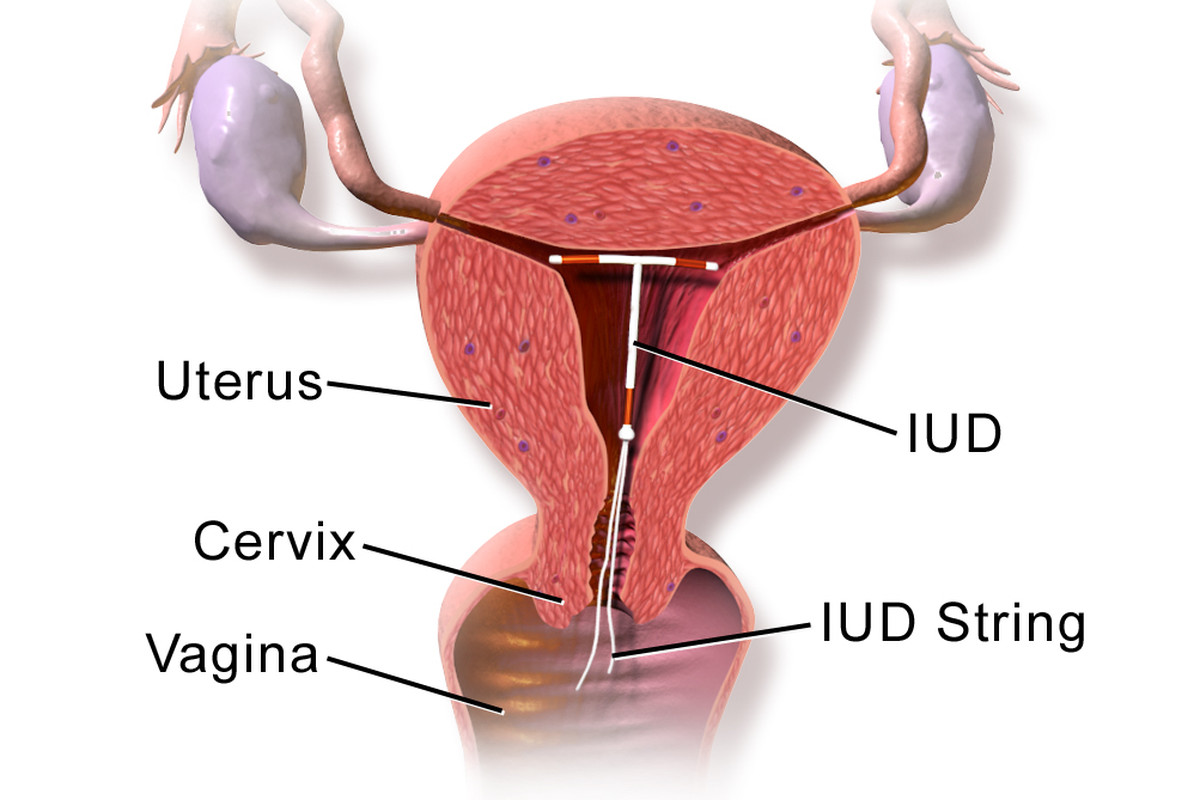
An intrauterine device is tiny and small. It is T-shaped, and the doctor places it inside the uterus. Out of the two varieties, you may choose between copper or hormonal one.
Hormonal IUD
The hormonal IUD releases pregnancy-stopping hormone (progestin) in the body. The function of this birth control is to thicken the cervical canal. The thickening of mucus disallows the sperm from mating an egg. Also, it prohibits the ovaries from releasing eggs.
So, fertilization does not happen. It also restricts the attachment of fertilized eggs (if any) to the uterus wall (endometrium). This is how the hormonal intrauterine devices stop you from conceiving.
Copper IUD
A Copper IUD does not contain any hormone. But it comes wrapped in a thin copper wire. This device is harmful to sperm. So, it destroys the sperm, not allowing it to fertilize the egg. It may also forbid implantation from taking place. In this manner, the device inhibits the possibility of a pregnancy.
For a better understanding of various types of IUDs read this article: IUD Types: What Are Different Types of IUDs?
Hormonal Implant
A hormonal implant is a birth control method. It is a tiny tube. Also, it is as small as a matchstick. The doctor will place it under your skin. Usually, the placement spot is the upper arm. The implant will release progestin in small amounts. This will restrict the ovary from giving out mature eggs.
Also, it will thicken the cervical mucus. With this, the sperm faces the impossibility to pass through and reach the egg for fertilization or implantation.
The Process to Insert an IUD or Implant
Here is how the nurse/doctor will insert an IUD or Implant:
Inserting an Intrauterine Device
The doctor will ask you to get a test for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or infections. This is in case you wish to get an intrauterine device in the uterus. If an IUD is placed inside when you have an STD, then the risk of PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease) increases. This can cause serious infections.
The doctor will widen the cervix or open it up a bit. This is to make the special tool go in through the cervix and place the IUD in the uterus. The entire procedure consumes only a few minutes. Some of the side effects are mild cramps. But these too last for a minute or two.
There are strings attached to the intrauterine device. These help the doctor to remove the device later. The process to insert and remove an IUD happens in the clinic. It is under the observation of a medical professional. You can self-initiate these procedures.
Inserting a Birth Control Implant
The doctor will insert the implant into your upper arm. He/she will firstly put a numbing medication at the insertion spot. The anaesthesia is usually injectable. Then the nurse will use a special device with the help of which he/she will insert the implant under your skin.
The procedure is short, lasting for a few minutes. There is no need for stitches afterwards. You will receive tips for how to care for the skin for a few days after getting the implant inserted on your arm. The implant may not be easily visible on the skin. However, you can feel it with your fingers.
Some of the side effects after placement include a bit of redness or soreness at the spot or slight bruising. But these go away soon. You need to visit a clinic for the insertion and removal of the implant.
Working of Implants and IUDs
Here are details about how long the birth control methods work:
- A Copper IUD can work effectively for up to 10 years.
- A hormonal one can stop you from conceiving up to 3 or 5 years.
- This depends on the manufacturer/brand.
- A hormonal implant, on the other hand, can stay active for up to 3 years.
Here is information on how soon these begin to function:
- A Copper Intrauterine Device will begin to work soon after placement in the uterus.
- The hormonal one too will work instantly if inserted in the initial 7 days of your period.
- A hormonal implant will work right away if placed in the initial 5 days of your period.
- You may get the implant later than this duration.
- If so, use a condom for a week or two to avoid conceiving.
Who Should Not Use These Contraception Options?
Every woman can safely get an implant or IUD. Even teenage females who have yet not given birth to a baby can use it. However, these birth control alternatives are unsafe for use in some women.
Do not use IUDs if:
- You have liver disease or tumour
- Cancer of uterus or cervix
- Vaginal bleeding if you are not menstruating
- Have AIDS
- Breast cancer
- Abnormal uterine anatomy
- Increase risk for Pelvic Inflammation Disorder or STD
- Are pregnant, or wish to conceive
It is not advisable to use a hormonal implant, if:
- Experience vaginal bleeding even when not menstruating
- You have a liver disease
- Are pregnant
- Have breast cancer
Side Effects of the Birth Control Devices
As understood, some amount of cramping is what you can expect during the insertion of an IUD. During placement of an implant, the skin may get sore or red. But besides these, here are a few more side effects, after birth control starts to work:
- Spotting between periods
- Irregular periods
- Headache
- Mood swings
- Change in body weight
If you choose a hormonal intrauterine device, then you may encounter lighter periods. Also, you can experience fewer cramps or cramps that hurt less. Other side effects may go away in a few months as the body adjusts to the hormone. Copper IUDs may lead to greater cramps, heavy bleeding, and bleeding between periods.
Heavy bleeding is not a common side effect of the implant. However, you may want to keep a track of the number of tampons or pads you use during menstruation. In case of unusual bleeding, contact your doctor. Implants may make your periods go away or become light.
Also, the birth control implant can ease pain and cramping. The most common encounter in the first 6 to 12 months of using the contraceptive is spotting. So, an implant relatively causes fewer side effects.
Risks of Implants and IUDs
Problems from any of these birth control options are rare. Sometimes, the IUD may push through the uterine wall. So, if you experience unusual pain after insertion, then contact your doctor. He/she will rectify the position of the IUD and reinsert it.
In a rare event, you may conceive when you are on an IUD. Such a kind of pregnancy is usually ectopic and develops outside the uterus. You need to get this pregnancy terminated as it could be life-threatening. Get an appointment with a doctor in case:
- Encounter constant pain
- Can feel the device in the cervix
- Cannot feel the IUD strings
- Foul smell or discharge from the vagina
In rare events, the implant may start to come out or move into the arm. If so, then the doctor will place the implant properly once again. Until then, start using another contraceptive such as a condom, right away.
Removal of Implants and IUDs
Every birth control method works for a duration. After this timeframe, you should restart the use of contraception if you want complete protection against pregnancy. Depending on the type of IUD you have, visit the doctor for its removal. For instance, after 10 years for a Copper IUD, or after 3 to 5 years for a hormone one.
For the removal of the implant, you need to visit the doctor after 3 years from the use of the device. The doctor will take all the necessary precautions during removal. Also, if you wish to not conceive further, then you can get a new IUD or Implant inserted any time you want.
To Conclude
Intrauterine devices and implants are two of the safest forms of birth control for women. The one that may work the best for you depends on your health, medical history, personal choice, and other factors. It is advisable to consult your healthcare provider to decide which one you must go ahead with.
April 2, 2021 Sam Bell











Comments